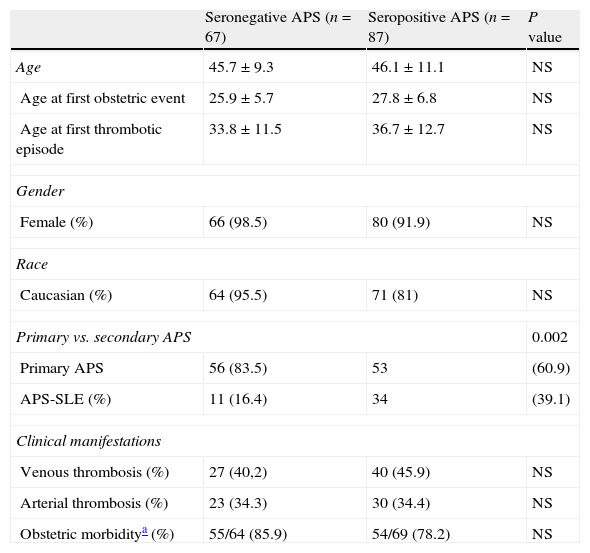
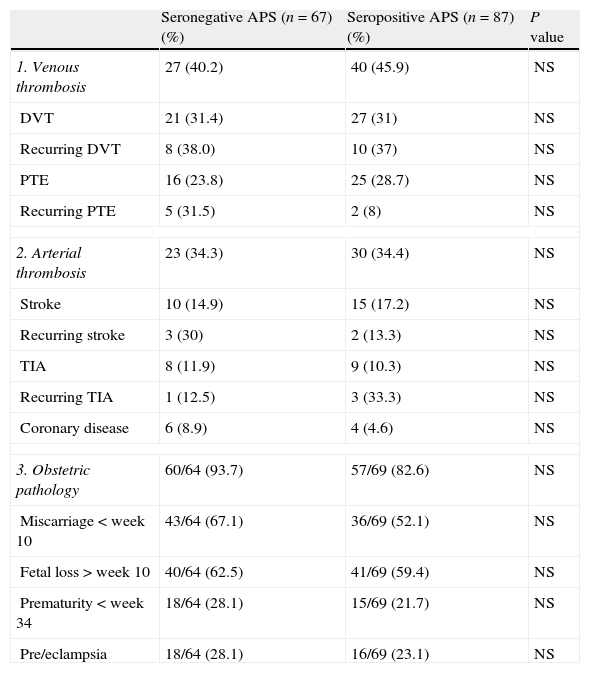
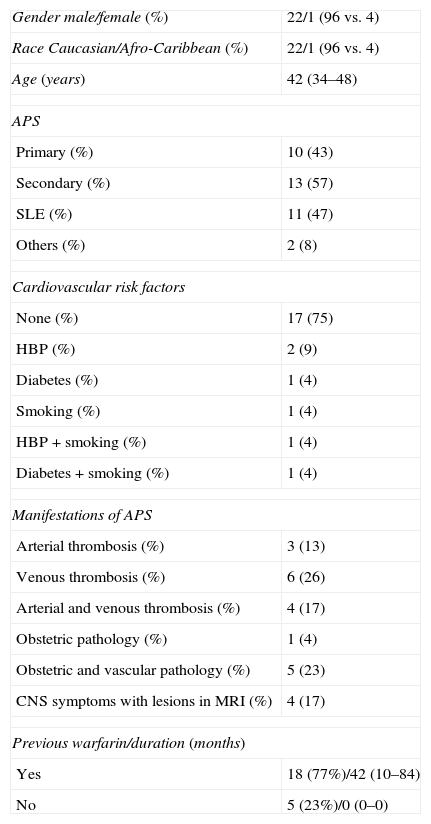
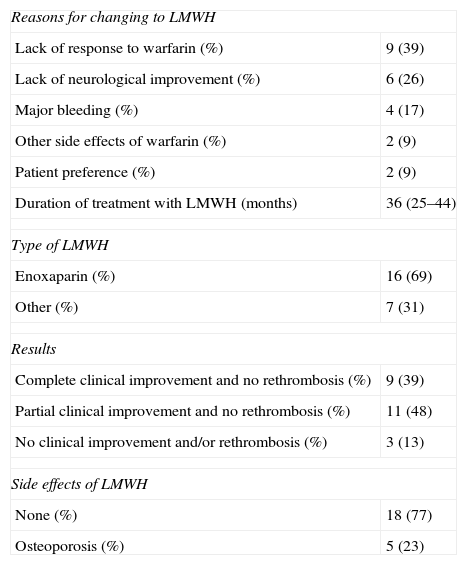
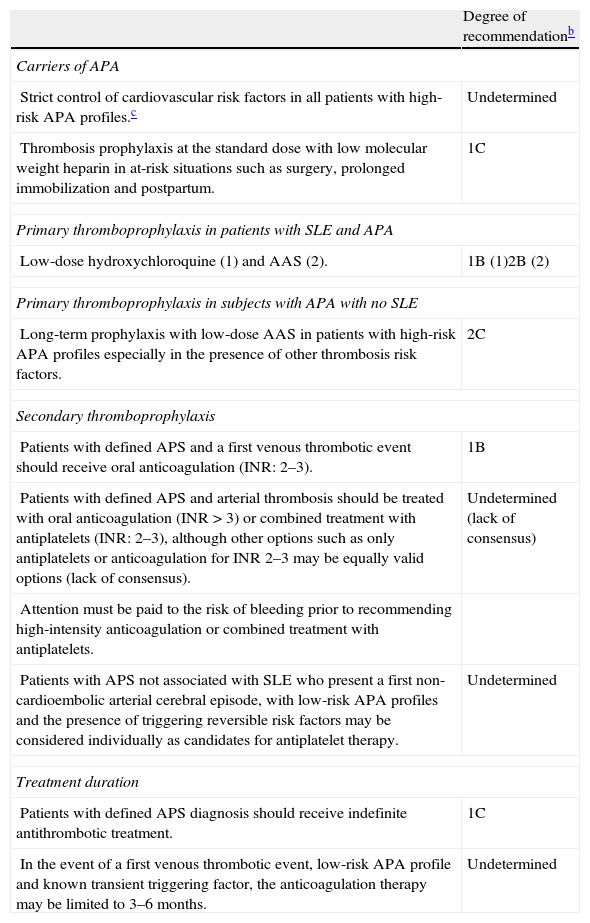
In this paper we review recent studies and consensus documents that we consider relevant to the diagnosis and treatment of patients with antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). The diagnosis of APS is based on the Sydney classification criteria (2006), in which positive laboratory tests (anticardiolipin antibodies, anti-β2-glycoprotein I antibodies or lupus anticoagulant) are mandatory. However, it is not uncommon to see patients with clinical features highly suggestive of the syndrome in whom these antibodies are persistently negative. Therefore, we summarize the principal clinical and serological findings in a subgroup of patients with seronegative APS in the first series published up to date. In addition, a recent study draws attention to the safety and efficacy of the long-term use of low-molecular-weight heparins in patients with APS not susceptible to warfarin treatment. There is also a subgroup of women with APS and recurrent fetal loss with no response to the standard antithrombotic therapy; in this group the materno-fetal prognosis could be improved by the addition of low-dose prednisolone during the first trimester of pregnancy. Finally, we list the principal recommendations regarding thromboprophylaxis in APS drawn from the expert consensus document elaborated at the meeting held in Galvestone (2010).
En este artículo se repasan algunos de los estudios y documentos de consenso recientes que hemos creído relevantes en el ámbito del diagnóstico y tratamiento de los pacientes con síndrome antifosfolípido (SAF). El diagnóstico del SAF se basa en los criterios de clasificación de Sidney (2006), donde la positividad de las pruebas de laboratorio (anticuerpos anticardiolipina, anti-β2-glicoproteína 1 o anticoagulante lúpico) supone un requisito necesario. Sin embargo, no es infrecuente encontrar pacientes con clínica muy sugestiva del síndrome y ausencia de estos anticuerpos. En este sentido, resumimos los principales hallazgos clínicos y serológicos de un subgrupo de pacientes con SAF seronegativo en la primera serie publicada hasta la actualidad.
En relación con el tratamiento antitrombótico, un estudio reciente ha señalado la seguridad y eficacia del uso de heparinas de bajo peso molecular a largo plazo en pacientes con SAF no subsidiarios de tratamiento con dicumarínicos. Por otro lado, existe un subgrupo de pacientes con SAF y pérdidas fetales recurrentes, cuyo pronóstico materno-fetal puede verse mejorado con la administración de bajas dosis de esteroides durante el primer trimestre de gestación. Finalmente, recogemos las principales recomendaciones sobre tromboprofilaxis en el SAF extraídas del consenso de expertos de la reunión celebrada en Galvestone (2010).
Artículo
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<