La hiperpotasemia (K+≥5,5mmol/l) es un desequilibrio iónico grave cuando aparece en pacientes que padecen insuficiencia cardiaca con fracción de eyección deprimida (ICFED), ya que incrementa el riesgo de fibrilación ventricular. No existen estimaciones del número de pacientes que sufren esta complicación. El objetivo de este estudio fue estimar la prevalencia e incidencia de hiperpotasemia en pacientes con ICFED en España.
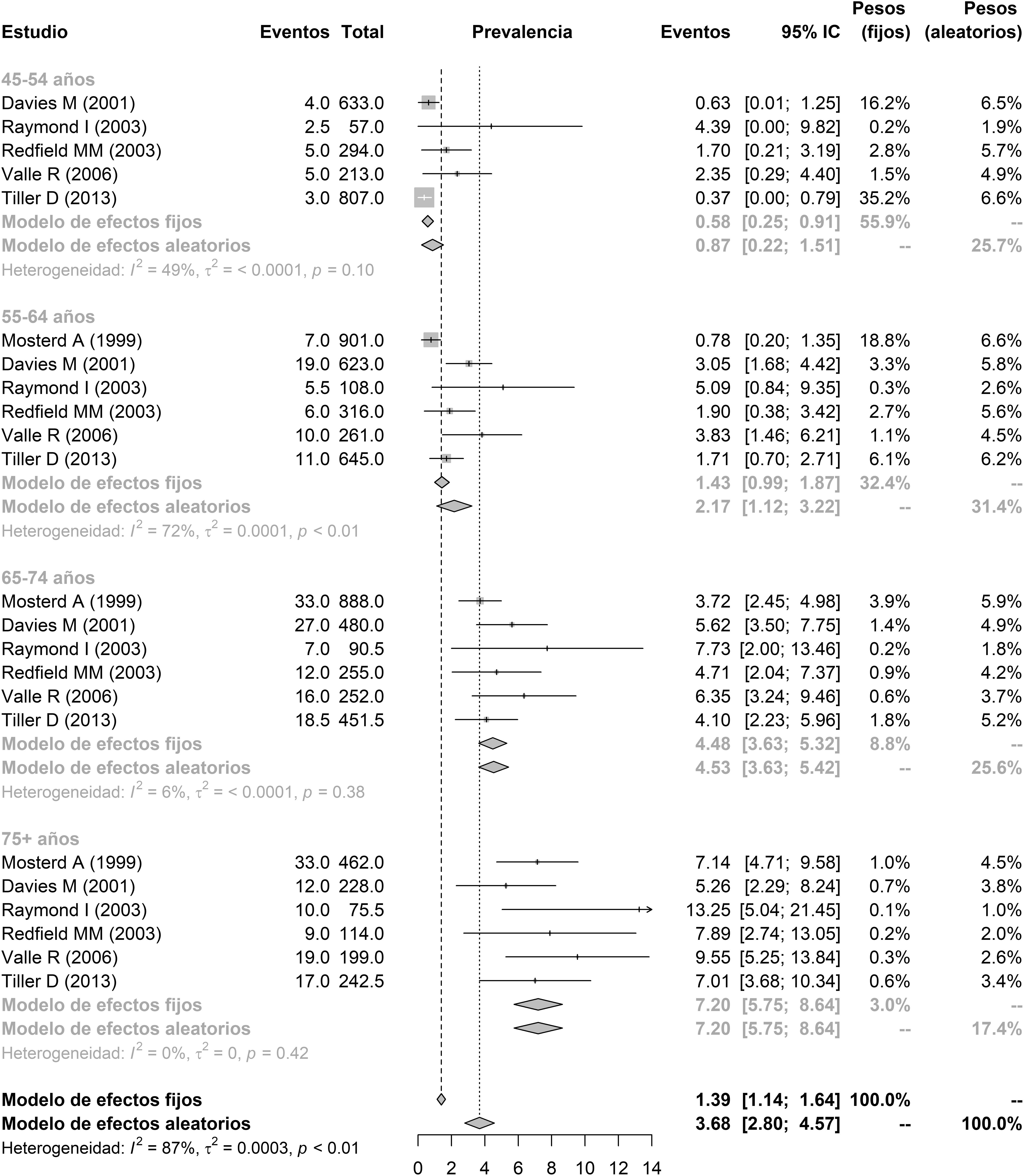
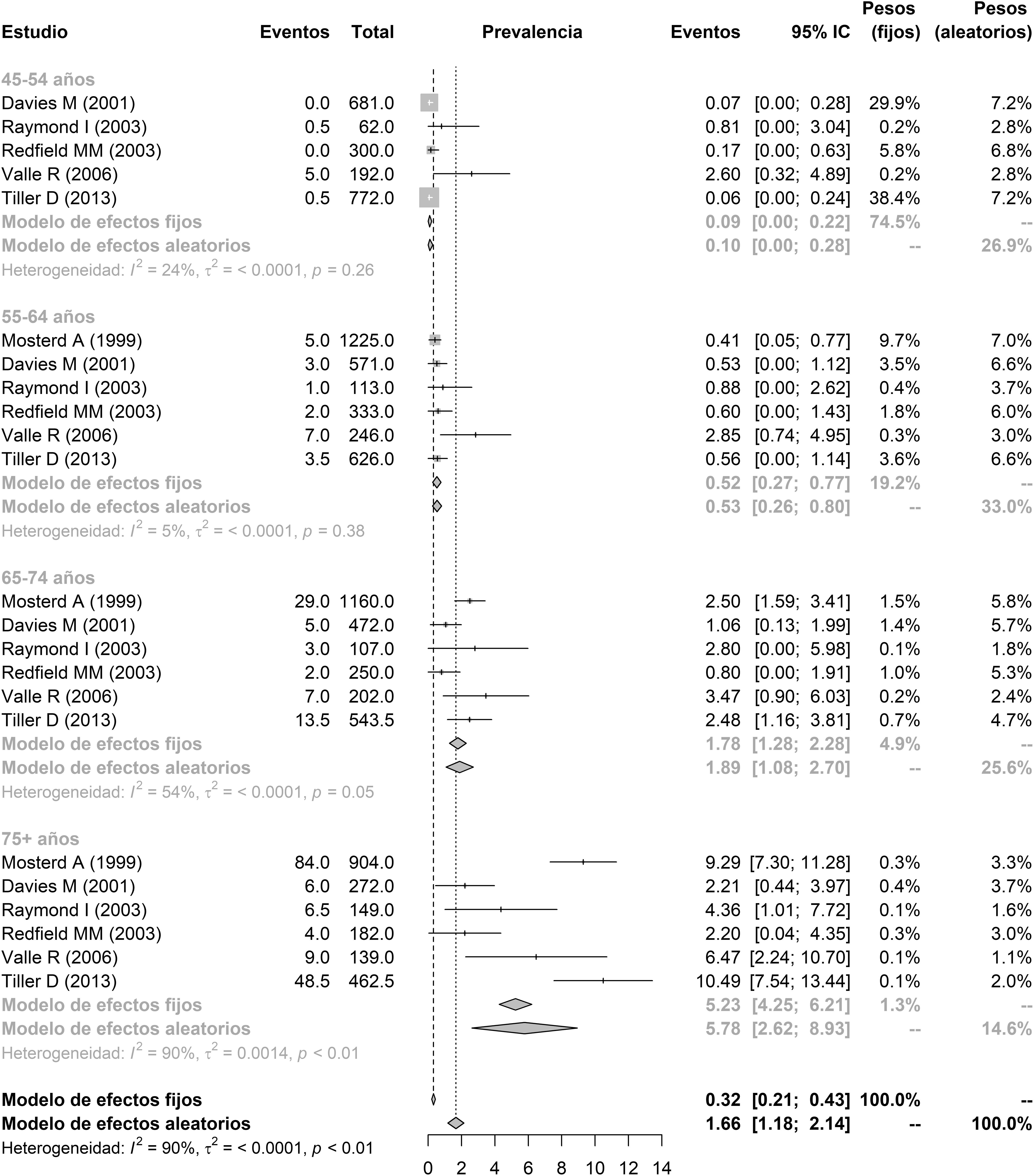
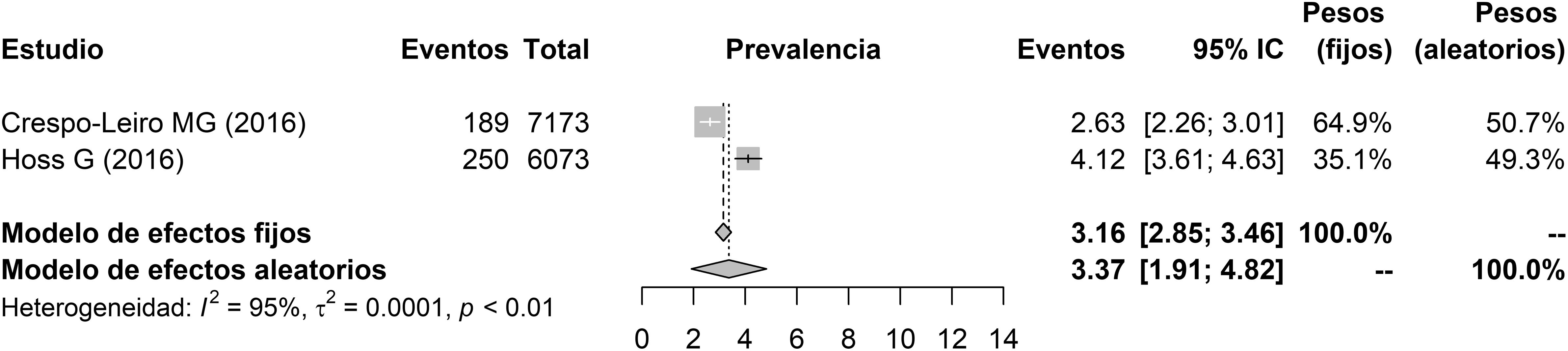
Materiales y métodosA partir de una búsqueda bibliográfica sistemática se calculó mediante un metaanálisis la prevalencia de ICFED<40% en población europea y norteamericana. A partir de otra búsqueda bibliográfica sistemática se calculó la prevalencia de hiperpotasemia en individuos con insuficiencia cardiaca, así como su incidencia anual. Considerando los anteriores valores y la pirámide de población española en 2016 se estimó el número de individuos con ICFED que presentan actualmente y que desarrollan cada año hiperpotasemia en España.
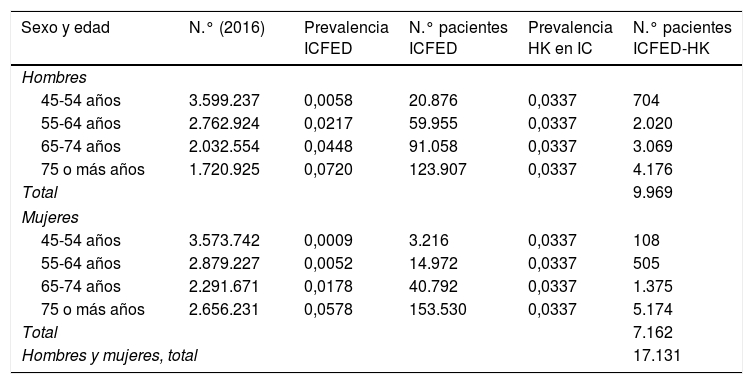
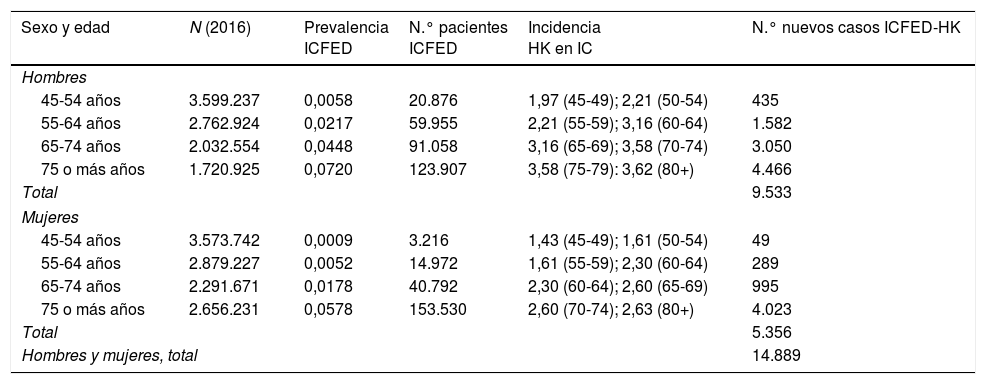
ResultadosAlrededor de 17.100 individuos (10.000 hombres y 7.100 mujeres) de los 508.000 pacientes con ICFED presentan hiperpotasemia en España. Asimismo, unos 14.900 pacientes con ICFED (9.500 hombres y 5.400 mujeres) la desarrollan cada año.
ConclusionesAproximadamente uno de cada 30 pacientes con ICFED presenta valores plasmáticos de potasio por encima de 5,5mmol/l.
Hyperkalaemia (K+ levels≥5.5mmol/L) is a severe ion imbalance that occurs in patients who have heart failure (HF) with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and increases the risk of ventricular fibrillation. Given that there are no estimates on the number of patients with this complication, the aim of this study was to estimate the prevalence and incidence of hyperkalaemia in patients with HFrEF in Spain.
Material and methodsBased on a systematic literature search and through a meta-analysis, we calculated an HFrEF prevalence of ≤40% in the European and U.S. population. Based on another systematic literature search, we calculated the prevalence of hyperkalaemia in patients with HF and its annual incidence rate. Considering the previous values and the Spanish population pyramid in 2016, we estimated the number of individuals with HFrEF who currently have hyperkalaemia and those who develop it each year in Spain.
ResultsApproximately 17,100 (10,000 men and 7100 women) of the 508,000 patients with HFrEF in Spain have hyperkalaemia. Furthermore, approximately 14,900 patients with HFrEF (9500 men and 5400 women) develop hyperkalaemia each year.
ConclusionsApproximately 1 of every 30 patients with HFrEF has plasma potassium values >5.5 mmol/L.
Artículo
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<