Alcohol consumption promotes inflammation through the Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)/nuclear factor (NF)-κB pathway, leading to organic damage. Some micro-RNA (miRNA) molecules modulate this inflammatory response by downregulating TLR4/NF-κB pathway mediators, like interleukins (ILs). Thus, polymorphisms within IL genes located near miRNA binding sites could modify the risk of ethanol-induced damage. The present study analyzed potential relationships between alcoholism or alcoholic liver disease (ALD) and IL12B 2124 G>T (rs1368439), IL16 5000 C>T (rs1131445), IL1R1 3114 C>T (rs3917328), and NFKB1 3400 A>G (rs4648143) polymorphisms.
Patients and methodsThe study included 301 male alcoholic patients and 156 male healthy volunteers. Polymorphisms were genotyped using TaqMan® PCR assays for allelic discrimination. Allele and genotype frequencies were compared between groups. Logistic regression analysis was performed to analyze the inheritance model.
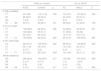
ResultsAnalysis of the IL1R1 (rs3917328) polymorphism showed that the proportion of allele T carriers (CT and TT genotypes) was higher in healthy controls (9.7%) than in alcoholic patients (6.5%; p=.042). However, multivariable logistic regression analyses did not yield a significant result. No differences between groups were found for other analyzed polymorphisms.
ConclusionsOur study describes, for the first time, the expected frequencies of certain polymorphisms within miRNA-binding sites in alcoholic patients with and without ALD. Further studies should be developed to clarify the potential relevance of these polymorphisms in alcoholism and ALD development.
El consumo de alcohol induce una respuesta inflamatoria mediada por los receptores de tipo Toll 4 (TLR4) y el factor nuclear (NF)-κB, originando daño orgánico. Algunos micro-ARN (miARN) modulan la respuesta inflamatoria mediante retroalimentación negativa de mediadores como las interleucinas (IL). Así pues, polimorfismos en los genes de algunas IL localizados cerca de las dianas de los miARN podrían modificar el riesgo de daño orgánico inducido por el alcohol. Este estudio analizó la posible relación entre el alcoholismo o la enfermedad hepática alcohólica (EHA) y los polimorfismos IL12B 2124 G>T (rs1368439), IL16 5000 C>T (rs1131445), IL1R1 3114 C>T (rs3917328) y NFKB1 3400 A>G (rs4648143).
Pacientes y métodosSe incluyeron 301 pacientes alcohólicos varones y 156 voluntarios sanos varones. Los polimorfismos fueron genotipados mediante discriminación alélica utilizando el sistema de PCR TaqMan®. Se compararon las frecuencias alélicas y genotípicas entre grupos y se realizó un análisis de regresión logística para dilucidar el modelo de herencia.
ResultadosEl análisis del polimorfismo de IL1R1 (rs3917328) mostró que la proporción de portadores del aleloT (genotipos CT y TT) era mayor en los controles sanos (9,7%) que en pacientes alcohólicos (6,5%, p=0,042). Sin embargo el análisis de regresión logística no mostró resultados significativos. No se encontraron diferencias significativas entre grupos con respecto al resto de polimorfismos estudiados.
ConclusionesNuestro estudio describe, por primera vez, las frecuencias esperadas de polimorfismos en regiones diana de miARN en pacientes alcohólicos con y sin EHA. Serán necesarios nuevos estudios para aclarar la relevancia de estos polimorfismos en el desarrollo de alcoholismo o EHA.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<