Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) worsens the prognosis for patients with an acute coronary event (ACE) treated with percutaneous coronary intervention. Objective: To assess the effect of COPD on arterial stiffness in patients with an ACE.
MethodsThe study included patients with an ACE treated with percutaneous coronary intervention. At 1 month, postbronchodilation spirometry was performed, and arterial stiffness and markers of myocardial damage (troponin T and ProBNP) were measured.
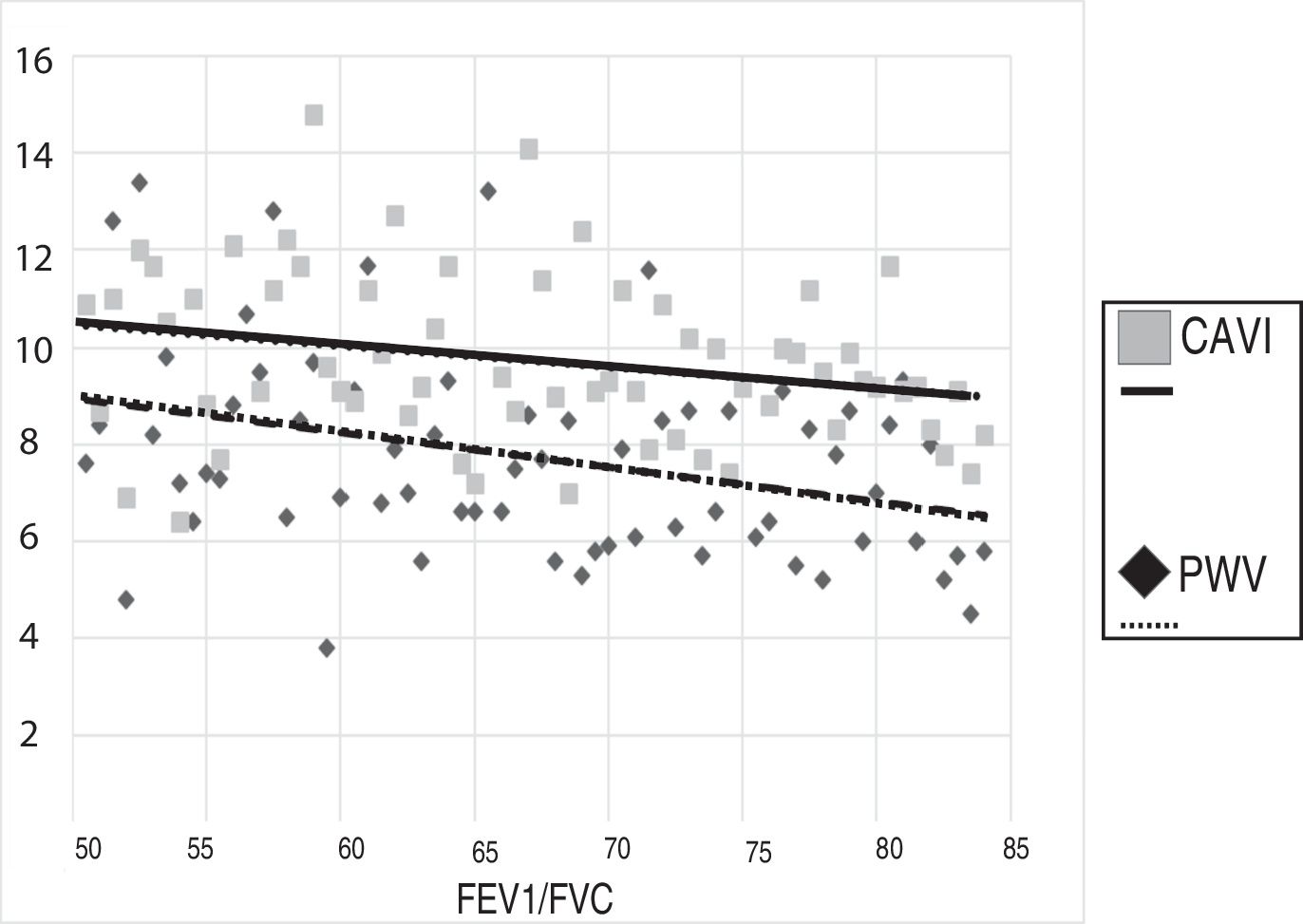
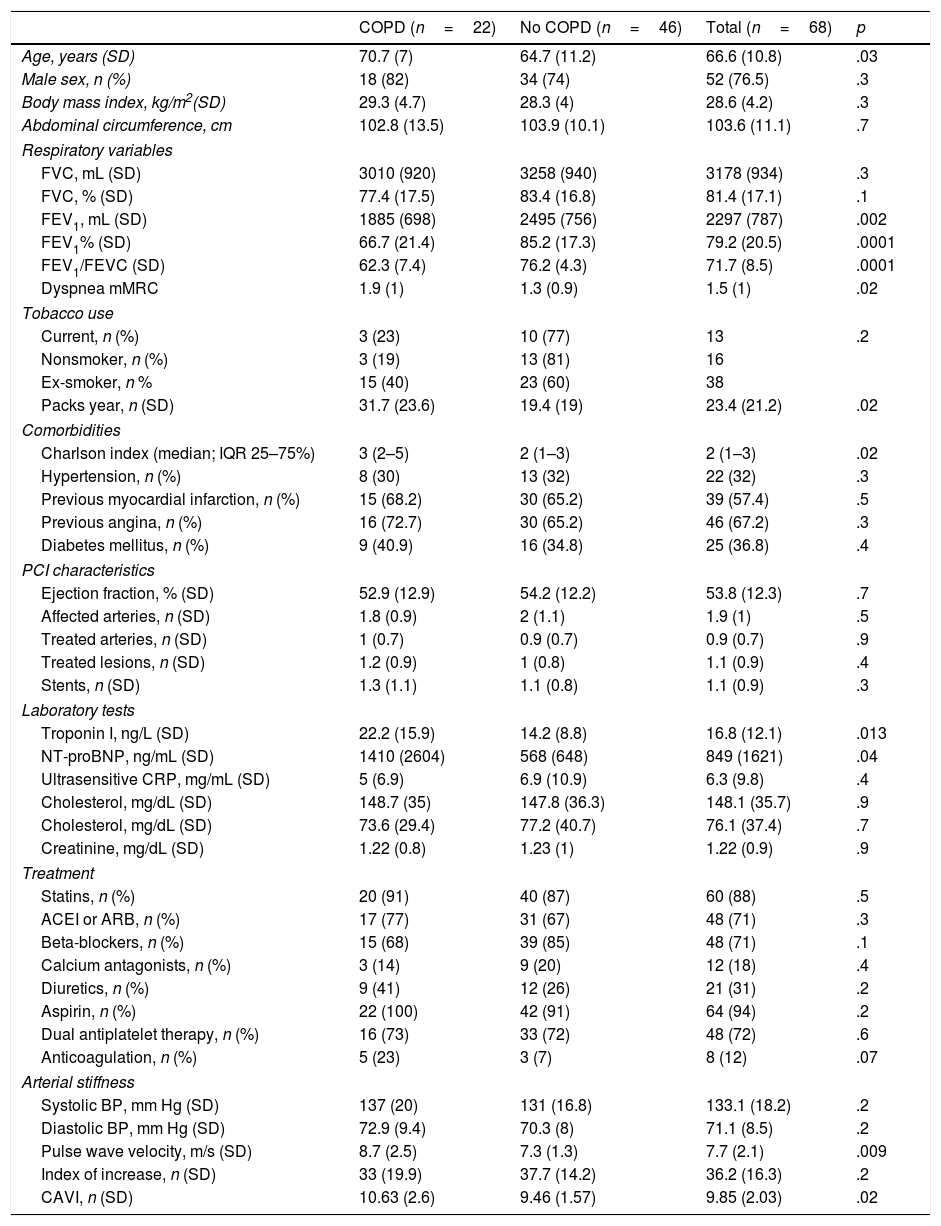
ResultsWe included 68 patients, 33% of whom had COPD (59% undiagnosed). The patients with COPD presented higher arterial stiffness values after adjusting for age and blood pressure readings. The troponin T and ProBNP levels were higher in the patients with COPD.
ConclusionsArterial stiffness is greater in patients with an ACE if they have concomitant COPD. These findings can help explain the poorer prognosis of patients with both conditions.
La enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica (EPOC) empeora el pronóstico de los pacientes con un evento coronario agudo (ECA) tratado con intervención coronaria percutánea. Objetivo: evaluar el efecto de la EPOC sobre la rigidez arterial en pacientes con un ECA.
MétodosPacientes con un ECA tratado con intervención coronaria percutánea. Al mes se realizó una espirometría posbroncodilatación y se determinó la rigidez arterial y marcadores de daño miocárdico (troponina T y ProBNP).
ResultadosSe incluyeron 68 pacientes, de los cuales un 33% tenían EPOC (59% no diagnosticados). Los pacientes con EPOC presentaron valores más altos de rigidez arterial tras ajustar por edad y cifras tensionales. Los niveles de troponina T y ProBNP fueron más altos en los pacientes con EPOC.
ConclusionesLa rigidez arterial es mayor en los pacientes con un ECA si tienen EPOC concomitante. Estos hallazgos pueden ayudar a explicar el peor pronóstico de los pacientes con ambas patologías.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<