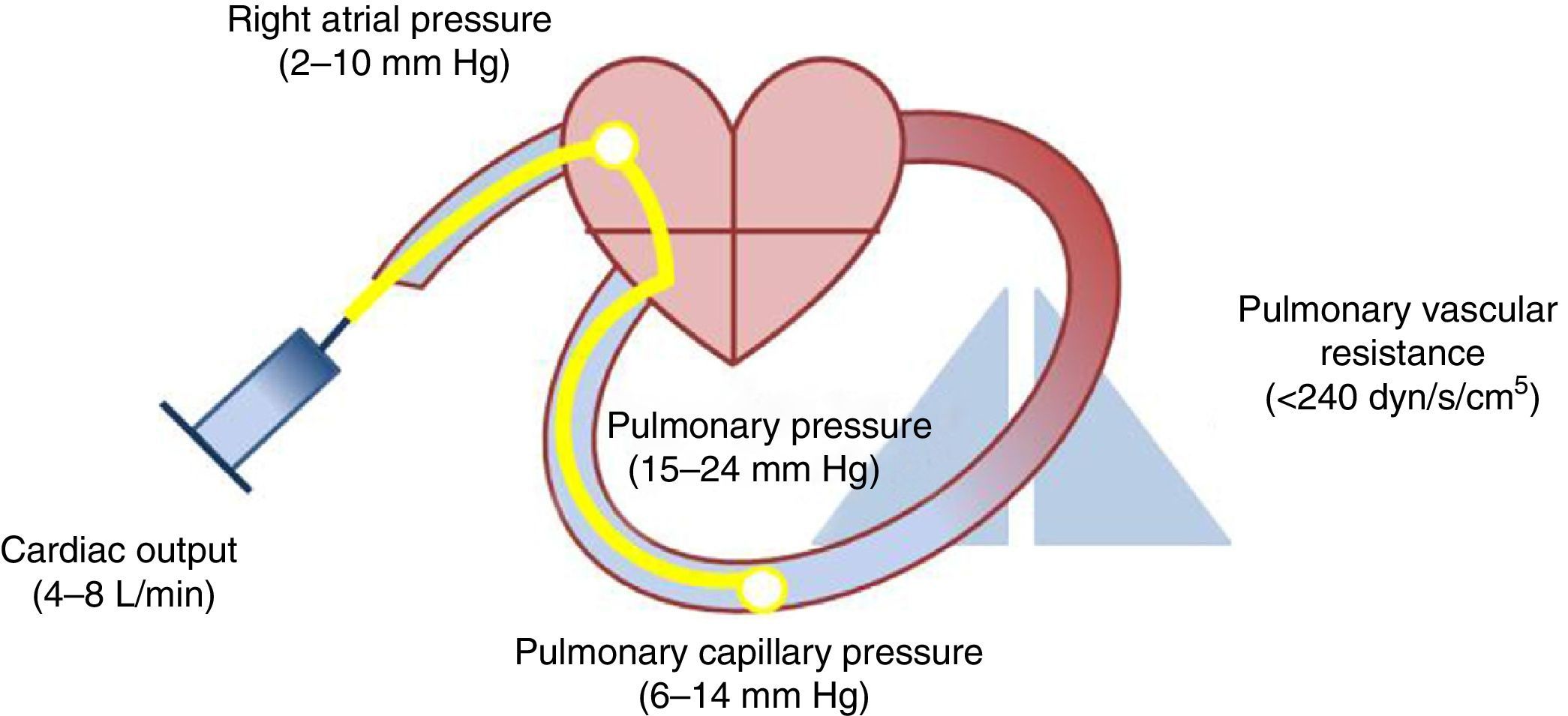
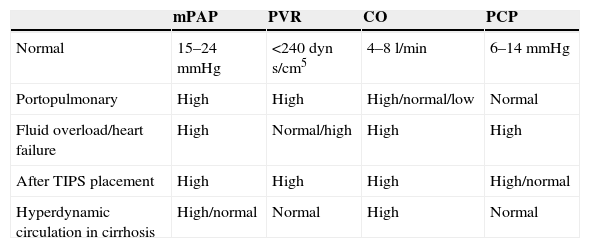
Pulmonary hypertension is a relatively common phenomenon in patients with hepatic cirrhosis and can appear through various mechanisms. The most characteristic scenario that binds portal and pulmonary hypertension is portopulmonary syndrome. However, hyperdynamic circulation, TIPS placement and heart failure can raise the mean pulmonary artery pressure without increasing the resistances. These conditions are not candidates for treatment with pulmonary vasodilators and require a specific therapy. A correct assessment of hemodynamic, ultrasound and clinical variables enables the differential diagnosis of each situation that produces pulmonary hypertension in patients with cirrhosis.
La hipertensión pulmonar es un fenómeno relativamente frecuente en los enfermos con cirrosis hepática y puede aparecer por diversos mecanimos. El escenario más característico que une la hipertensión portal y la hipertensión pulmonar es el síndrome portopulmonar. Sin embargo, la circulación hiperdinámica, la colocación de un TIPS o la insuficiencia cardíaca pueden elevar la presión media de la arteria pulmonar sin incremento de las resistencias. Estas situaciones no serán candidatas a tratamiento con vasodilatadores pulmonares y requieren una terapéutica específica. Una correcta valoración de variables hemodinámicas, ecográficas y clínicas permite el diagnóstico diferencial entre cada situación que produce hipertensión pulmonar en los pacientes cirróticos.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<