El control de los factores de riesgo cardiovascular es especialmente importante en diabetes tipo 2 (DM-2). El grado de control no se ha estudiado específicamente en población rural ni cómo afecta a la calidad de vida. Hemos valorado el grado de consecución de los principales objetivos de control en el área adscrita a un hospital comarcal y evaluado la calidad de vida.
Material y métodosEstudio transversal, en pacientes DM-2 atendidos en atención primaria de las comarcas Pallars Jussà y Sobirà (Lleida). Se evaluaron el tabaquismo, IMC, PA, HbA1c, colesterol total, c-LDL, c-HDL y triglicéridos. La calidad de vida se valoró con cuestionario de salud (EQ-5D).
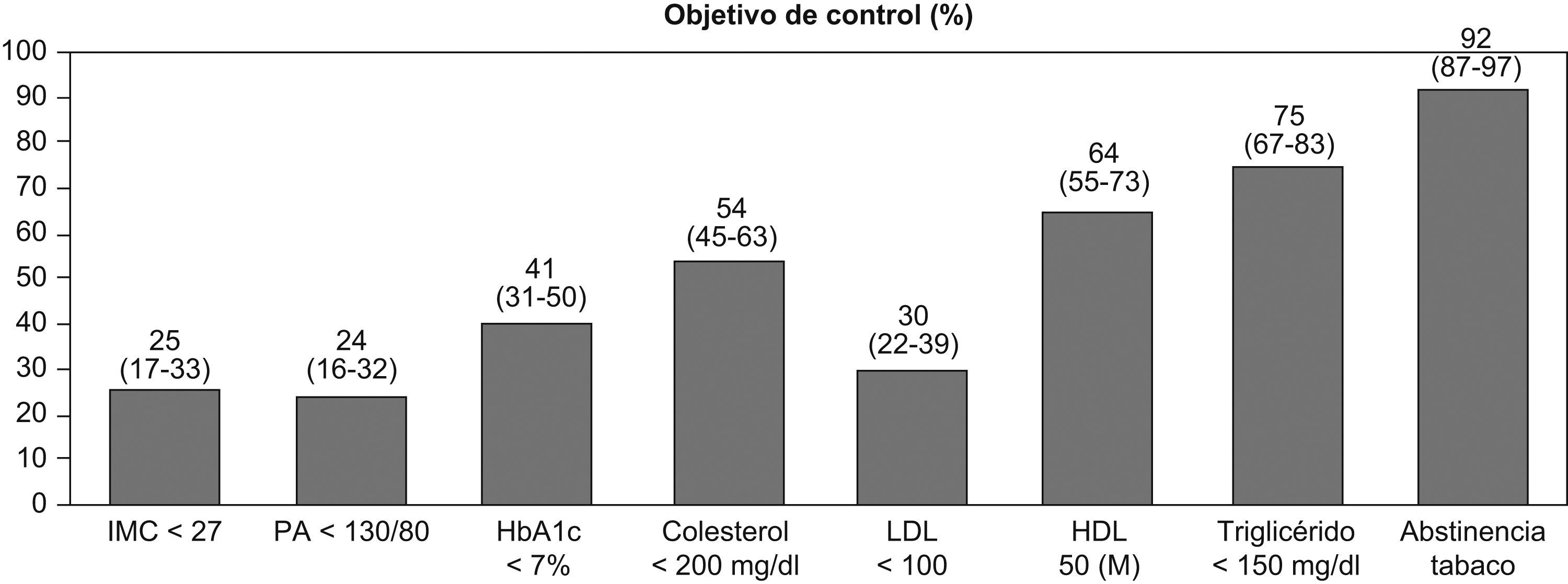
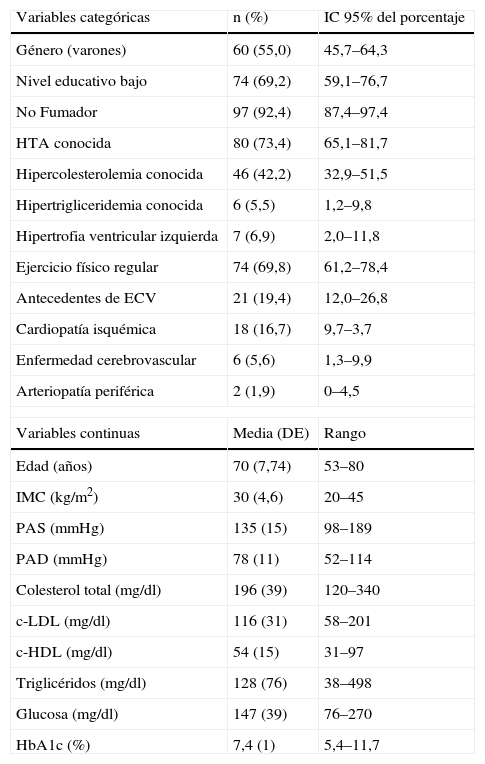
ResultadosSe incluyeron 109 sujetos (55% hombres) con edad media (desviación estándar) de 70 (7,7) años. El 25% de los casos tenía IMC <27kg/m2 y 92% no fumaba. La PA sistólica y diastólica se hallaron controladas en el 36% y 53%, y la HbA1c, en 41%. Se halló control óptimo del colesterol total en el 54%, c-LDL en el 30%, c-HDL en el 64% y triglicéridos en el 75%. Un 1,8% alcanzaban todos los objetivos. La media de la valoración subjetiva global del estado de salud fue 69 puntos.
ConclusionesUna proporción muy pequeña de los pacientes con DM-2 se encuentran en los objetivos recomendados. Los más difíciles de conseguir fueron IMC y PA y los de mayor consecución fueron el nivel de triglicéridos y abstinencia tabáquica. La percepción subjetiva del estado de salud no se asoció al grado de control de objetivos.
Control of cardiovascular risk factors is especially important in type 2 diabetes (DM2). The degree of control has not been studied specifically in rural population and how it affects quality of life. We have assessed the degree of accomplishment of the main control objectives in the area assigned to a regional hospital and evaluated their quality of life.
Material and methodsCross-sectional study, in DM2 patients seen in Primary Care Centers on the Pallars Jussà y Sobirà (Lleida) regions. Smoking, body mass index (BMI), blood pressure (BP), HbA1c, total cholesterol, LDLc, HDL-c and triglycerides were evaluated. Quality of life was assessed with a health questionnaire (EQ-5D).
Results109 subjects (55% male) were recruited, with a medium age (standard deviation) of 70 (7.7) years old. 25% of cases had BMI <27kg/m2 and 92% were non-current smokers. Systolic and diastolic BP were under control on the 36% and 53%, and HbA1c, on the 41%. Total Cholesterol was found optimal on the 54%, LDL-c on the 30%, HDL-c on the 64% and triglycerides on the 75%. 1.8% of patients achieved all the goals. The medium global subjective assessment of health status was 69 points.
ConclusionsA very small percentage of patients with DM2 are in the recommended target. The most difficult to achieve were BMI and BP and the highest achievement were triglycerides and smoking abstinence. Subjective perception of health status was not associated with degree of objectives’ control.
Artículo
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<