Los acontecimientos adversos causados por medicamentos (AAM) son un problema de salud pública, cuya magnitud es difícil de cuantificar debido a su infranotificación. Nuestro objetivo fue identificar y describir los AAM registrados en el conjunto mínimo básico de datos de los servicios de medicina interna durante los años 2005–07.
Pacientes y métodosEstudio transversal. Se seleccionaron los episodios codificados, según la CIE-9-MC, como tales en los informes de alta de todos los pacientes hospitalizados durante 2005–07 en todo el territorio español. Se describieron y analizaron las variables sociodemográficas, las categorías diagnósticas y los tipos de fármacos, entre otras.
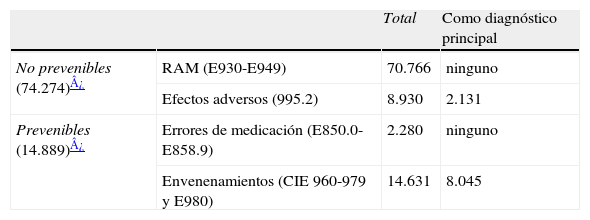
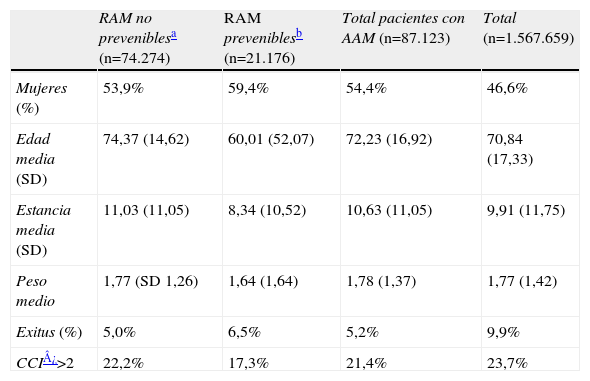
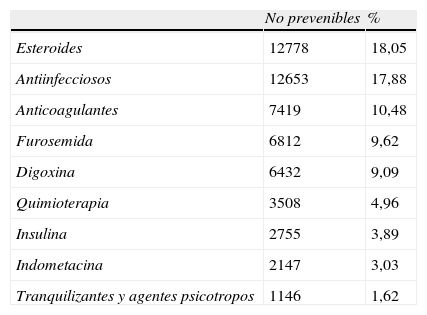
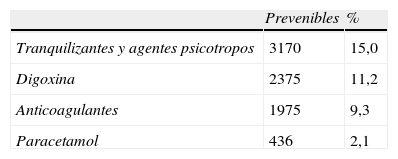
ResultadosDe las 1.567.659 altas codificadas en el conjunto mínimo de datos, se registraron 96.607 AAM en 86.880 episodios (5,55%) de los cuales un 82,86% eran no prevenibles y un 17,14% prevenibles. Un 4,5% de los episodios registraron una reacción adversa a medicamentos. Los AAM fueron más frecuentes en mujeres y la aparición de una reacción adversa a los medicamentos durante el ingreso se acompaña de prolongación de la estancia hospitalaria.
ConclusionesEl conjunto mínimo básico de datos es una herramienta útil para la identificación, la cuantificación y el análisis de las reacciones adversas a los medicamentos, aunque limitada por el bajo registro en los informes de alta.
Adverse drug events (ADE) are a public health problem, the dimension of which is difficult to quantify because it is under-reported. We have aimed to identify and describe the ADEs recorded in the minimum basic data set (MBDS) of the Internal Medicine Services during the years 2005–7.
Patients and methodsA cross-sectional study. Those episodes coded as such, according to the ICD-9-CM, in the discharge reports of all the patients hospitalized during 2005–07 in the entire Spanish territory, were selected. The sociodemographic variables, diagnostic categories and types of drugs, among others, were described and analyzed.
ResultsOf the 1,567,659 discharges coded in the Minimum Basic Data Set" (MBDS), 96,607 ADEs were recorded in 86,880 episodes (5.55%). Of these 82.86% were not preventable and 17.14% were preventable. A total of 4.5% of the episodes recorded an adverse drug reaction (ADR). The ADE's were more frequent in women and the appearance of an ADR during admission was accompanied by an increase in the hospital stay.
ConclusionsThe MBDS is a useful tool for the identification, quantification and analysis of the ADRs, however, it is limited by the low recording of the discharge reports.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<