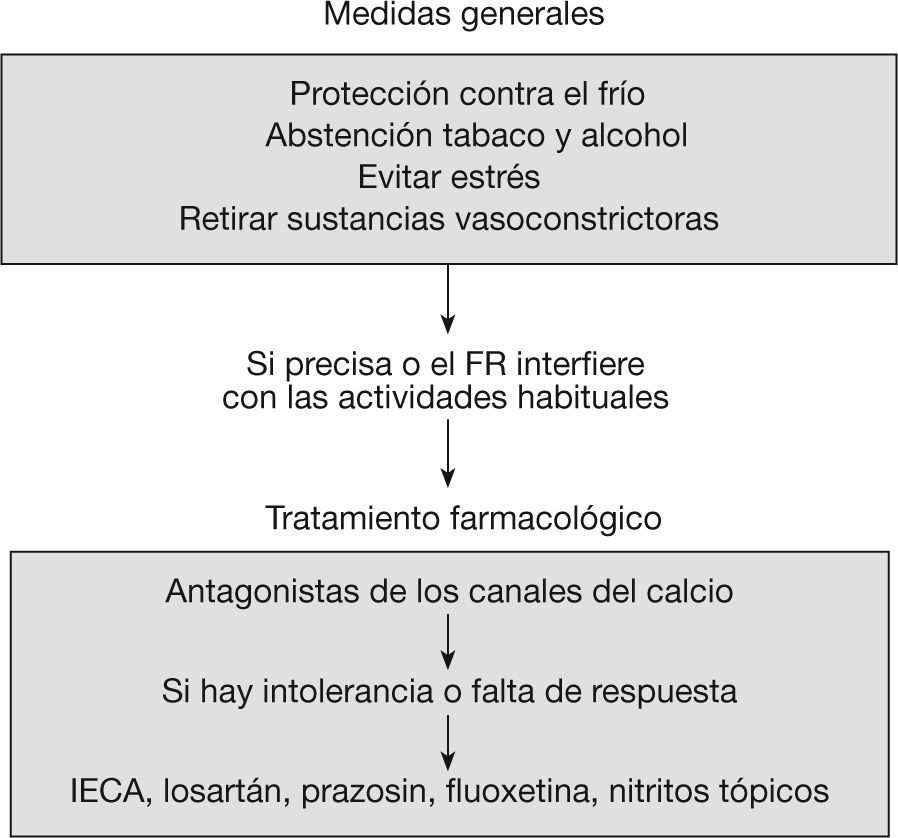
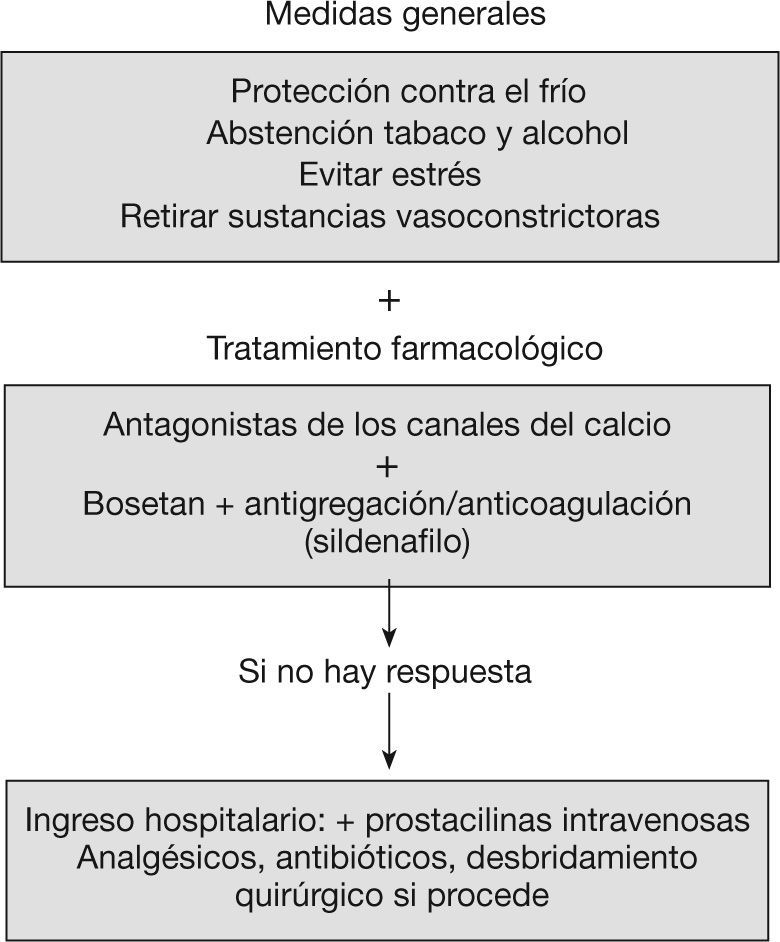
El fenómeno de Raynaud (FR) es un cuadro clínico caracterizado por la presencia de episodios recurrentes de vasospasmo, que es desencadenado por el frío u otros estímulos y afecta especialmente a los dedos de las manos y/o pies. Puede ser primario o idiopático, o secundario y obedecer a muchas causas, entre las que destacan las conectivopatías y, en particular, la esclerodermia. El FR primario no requiere, en general, tratamiento farmacológico, sólo medidas generales. Los antagonistas de los canales del calcio continúan siendo los fármacos de primera elección. Sin embargo, cuando el FR es grave y se acompaña de úlceras digitales/necrosis hística, la pauta terapéutica ha de individualizarse y deben establecerse combinaciones con distintos fármacos como: prostanoides, bosentan, sildenafilo, antiagregantes/anticoagulantes, antibióticos y analgésicos.
Raynaud's phenomenon (RP) is a clinical picture characterized by the presence of recurrent episodes of vasospasm that is precipitated by cold or other stimuli and especially affects the fingers and/or toes. It may be primary or idiopathic or secondary and be due to many causes, among which connective diseases, and specifically scleroderma, stand out. Primary RP does not generally require drug treatment, only requiring general measures. Calcium channel antagonists continue to be the drug of first choice. However, when RP is severe and is accompanied by digital ulcers/tissue necrosis, the therapeutic regime must be individualized and combinations should be established with difference drugs such as prostanoids, bosentan, sildenafil, antiaggregants/anticoagulants, antibiotics and analgesics.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<