Genetic studies have shown associations of several single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) with different rates of progression and variation in susceptibility to HIV infection. This study aimed to estimate the frequency of ccr5Δ32, IL-6-174G/C, IFN-γ+874T/A and IL-10-1082A/G polymorphisms in Cuban HIV-infected patients and a group of sero-discordant couples to assess their influence on risk and disease progression.
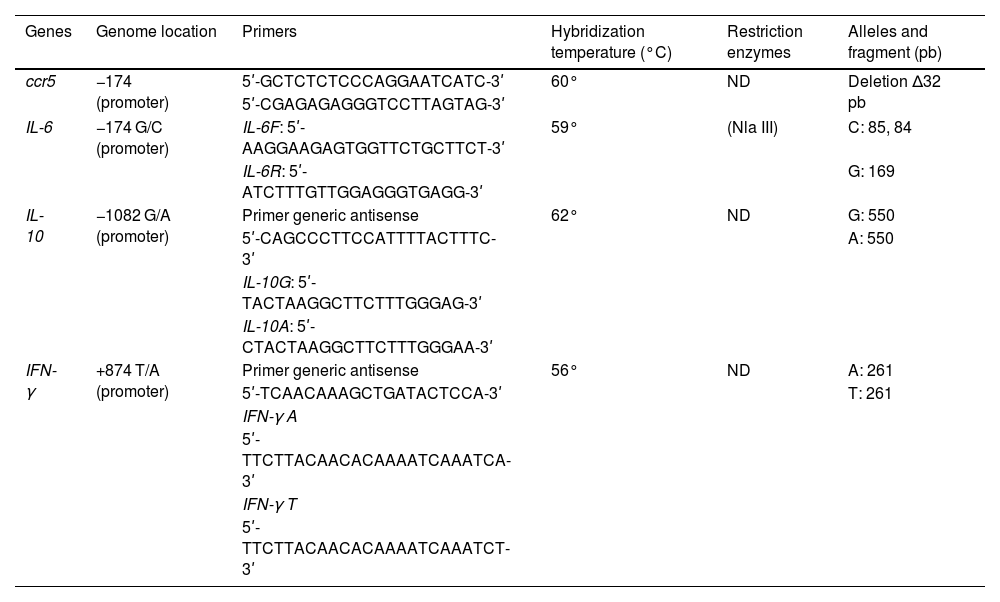
MethodsA cross-sectional study was carried out on 120 subjects registered at the Institute of Tropical Medicine «Pedro Kour» (IPK) and the Ameijeiras Hospital from June 2018 until December 2019. The amplification of fragments of the ccr5, IL-6, IFN-γ and IL-10 genes was performed by polymerase chain reaction followed by identification of polymorphisms using the restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis for IL-6 with the restriction enzymes Nla III. Amplification Refractory Mutation System was used for IFN-γ and IL-10 genes.
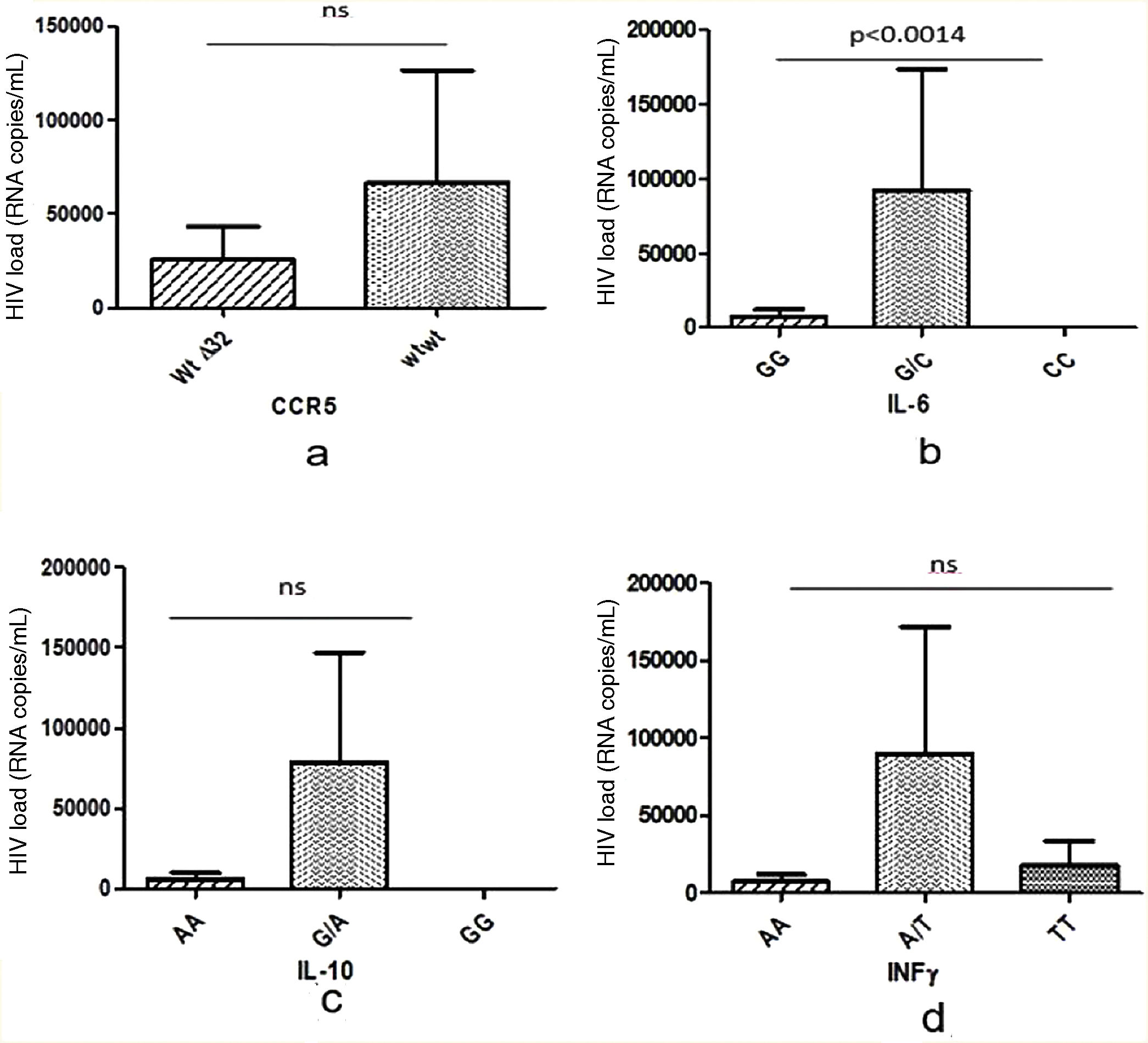
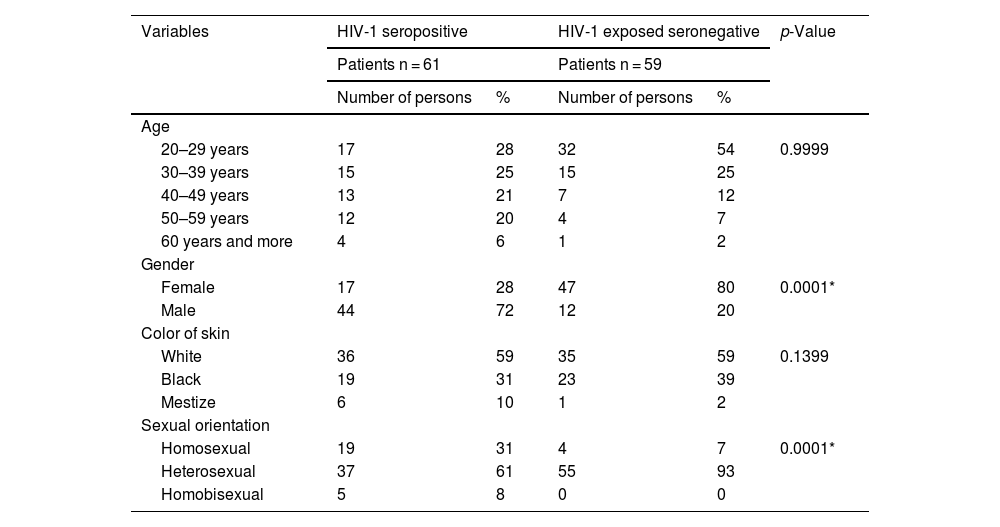
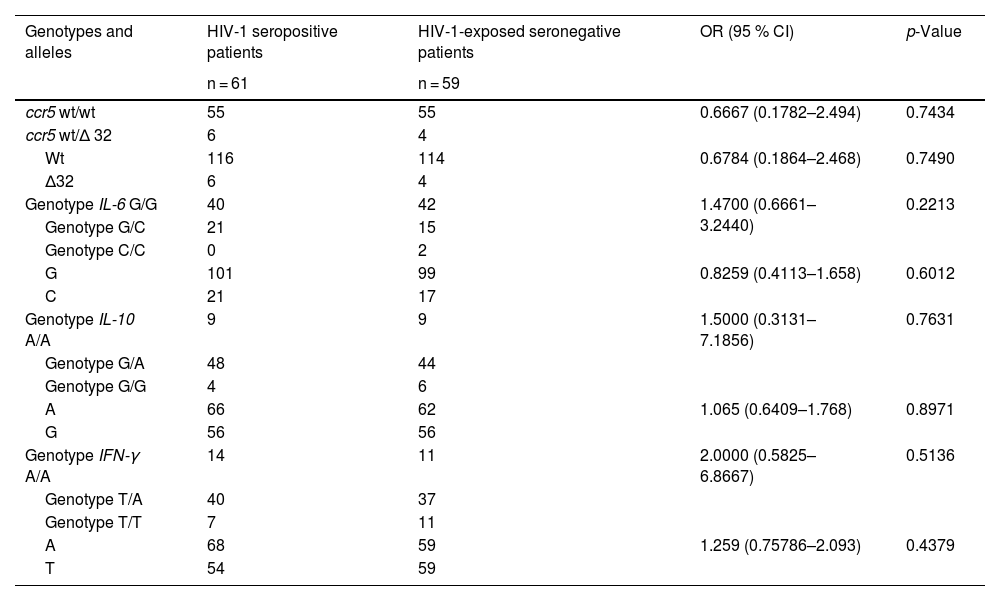
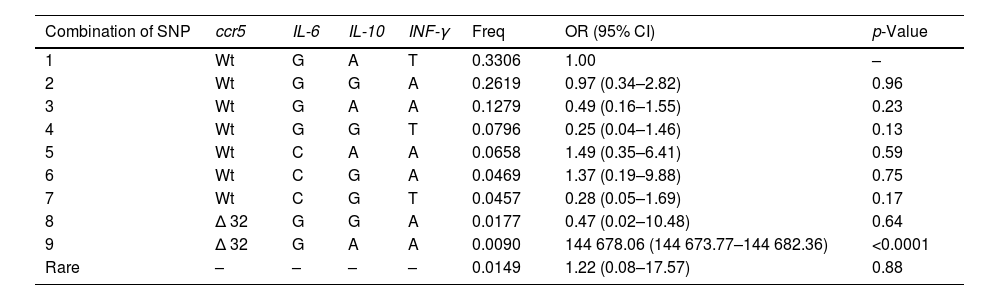
ResultsThe allelic and genotypic distributions of the genes ccr5, IL-6, IFN-γ and IL-10 did not differ significantly between the two groups. Cell counts and plasma viral load values did not differ significantly between genotypes of the ccr5, IL-6, IFN-γ and IL-10 genes. Only the IL-6 GC genotype was associated with higher viral load values. The combination of alleles of the four considered SNPs showed a highly significant increase in the risk of HIV infection for one of them, but with a very low frequency (<1%).
ConclusionThis study contributes to evaluating the frequency of these polymorphisms and their influence on biomarkers of the progression of HIV infection in the Cuban HIV-population.
Los estudios genéticos han demostrado asociaciones de varios polimorfismos de un solo nucleótido (SNP) con diferentes tasas de progresión y variación en la susceptibilidad a la infección por VIH. Este estudio tuvo como objetivo estimar la frecuencia de los polimorfismos ccr5Δ32, IL-6-174G/C, IFN-γ+874T/A e IL-10-1082A/G en pacientes cubanos infectados por VIH y un grupo de parejas serodiscordantes para evaluar su influencia sobre el riesgo y la progresión de la enfermedad.
MétodosSe realizó un estudio transversal en 120 sujetos atendidos en el Instituto de Medicina Tropical «Pedro Kour» (IPK) y el Hospital Hermanos Ameijeiras entre junio de 2018 y diciembre de 2019. La amplificación de los fragmentos de los genes ccr5, IL-6, IFN-γ e IL-10 se realizó mediante reacción en cadena de la polimerasa seguida por el análisis del polimorfismo de fragmentos de restricción utilizando la enzima Nla III para la IL-6. El Sistema de Mutación Refractario a la Amplificación por PCR se utilizó en el caso de los genes IFN-γ e IL-10.
ResultadosLas distribuciones alélicas y genotípicas de los genes ccr5, IL-6, IFN-γ e IL-10 no difirieron significativamente entre los dos grupos. Los recuentos celulares y los valores de carga viral en plasma no difirieron significativamente entre los genotipos de los genes ccr5, IL-6, IFN-γ e IL-10. Sólo el genotipo IL-6 GC se asoció con valores más altos de carga viral. La combinación de alelos de los cuatro SNP considerados mostró un aumento muy significativo del riesgo de infección por VIH para uno de ellos, pero con una frecuencia muy baja (< 1%).
ConclusiónEste estudio contribuye a evaluar la frecuencia de estos polimorfismos y su influencia en los biomarcadores de la progresión de la infección por VIH en la población cubana con infección por el VIH.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<