Evaluar las características de la enfermedad cardiovascular (ECV), el tratamiento y cumplimiento de los objetivos terapéuticos para la presión arterial y lípidos en pacientes hipertensos atendidos en Atención Primaria.
Pacientes y métodosEstudio transversal de todas las historias clínicas de pacientes hipertensos, a partir de las cuales se seleccionaron los enfermos en tratamiento farmacológico que consultaron en los 25 centros de Salud del Área 6 de Madrid.
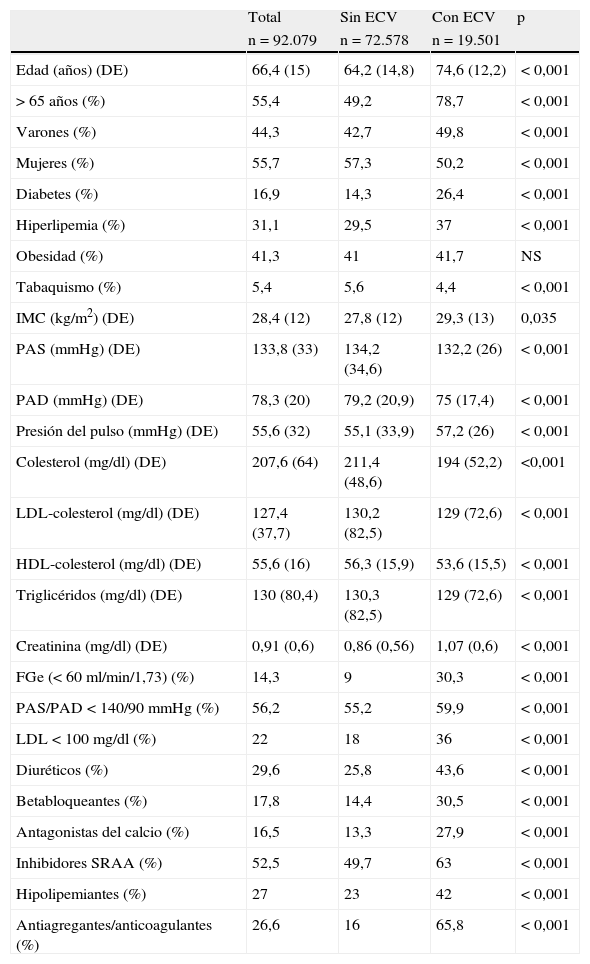
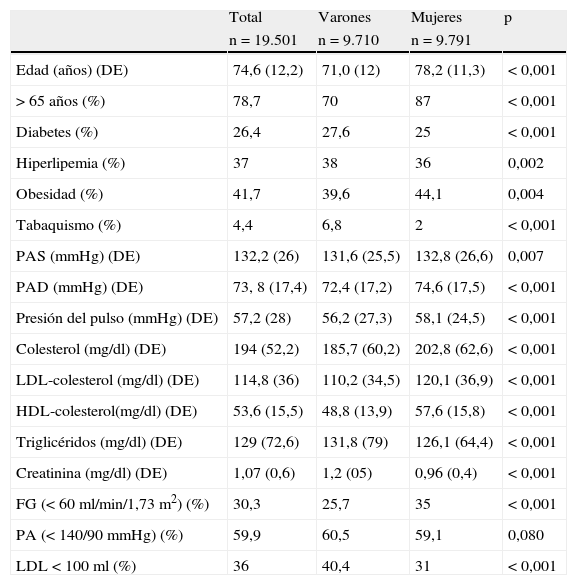
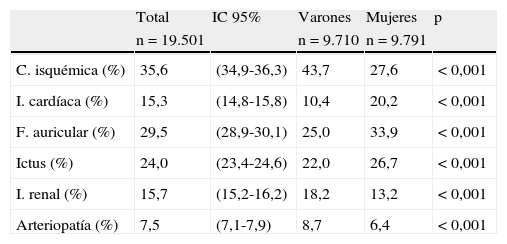
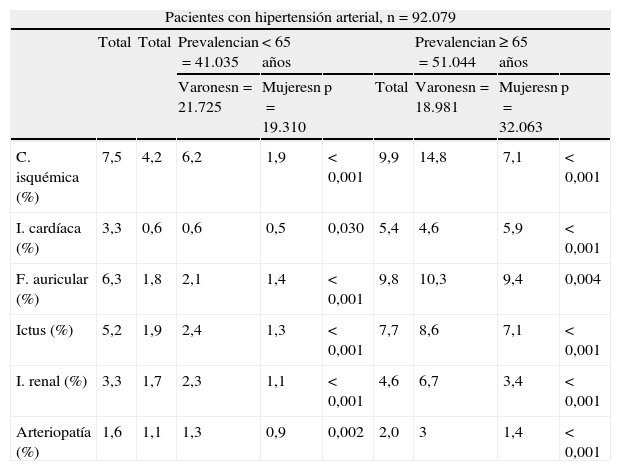
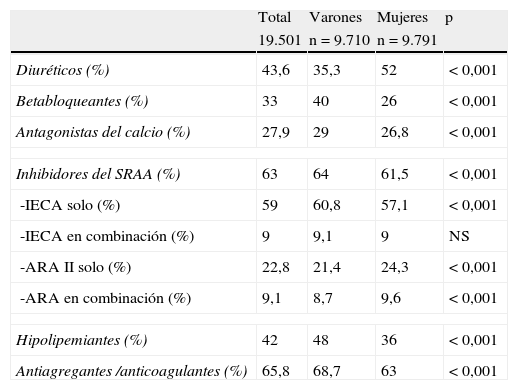
ResultadosDe 92.079 historias, 19.501 enfermos (21,2%) con hipertensión arterial (HTA) tenían un diagnóstico previo de ECV (23,9% eran varones y el 19,1% mujeres). En estos hipertensos con ECV los diagnósticos más frecuentes y su proporción en hombres y mujeres fueron: cardiopatía isquémica, 35,6% (43,7/27,6%); fibrilación auricular, 29,5% (25/33,9%); ictus, 24% (22/26,7%); insuficiencia renal, 15,7% (18,2/13,2%); insuficiencia cardíaca, 15,3% (10,4/20,2%); y enfermedad arterial periférica, 7,5% (8,7/6,4%) (p<0,05). En los hombres la prescripción de fármacos antihipertensivos, hipolipemiantes y antiagregantes fue mayor que en las mujeres, y en éstas predominó la prescripción de diuréticos, antagonistas de los receptores de la angiotensina y anticoagulantes (p<0,05). El porcentaje de hombres y mujeres con presión arterial<140/90mmHg fue del 60,5 y del 59,1%, y de LDL-colesterol < 100mg/dL, 40,4 y 31%, respectivamente.
ConclusionesEn los casi 20.000 hipertensos analizados por enfermedad cardiovascular, se observan diferencias apreciables de género en la prevalencia, tratamiento y consecución de objetivos terapéuticos en los diversas enfermedades cardiovasculares. Estos resultados sugieren la conveniencia de homogeneizar los registros informáticos, como el presente, para seguir los resultados en el tiempo, sin necesidad de realizar estudios por muestras.
To examine the type of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and treatment and achievement of treatment goals in blood pressure and lipids in hypertensive patients in primary care.
Patients and methodsA cross-sectional study of all medical records of hypertensive patients, from which patients with antihypertensive treatment who visited the 25 Primary Health Care Centers of the 6th sanitary district of Madrid during 2008 were selected.
ResultsFrom a total of 92,079 patients, 19,501 (21 2%) with an arterial hypertension had a previous diagnosis of CVD (23.9% in males and 19.1% in females). In hypertensive with CVD, the most frequent diagnosis and their proportion in males and females were: ischemic heart disease 35.6% (43.7%/27.6%), atrial fibrillation 29.5% (25%/33.9%), stroke 24% (22%/26.7%), chronic renal disease 15.7% (18.2%/13.2%), heart failure 15.3% (10.4%/20.2%) and peripheral artery disease 7.5% (8.7%/6.4%) (P<.05). Antihypertensive drugs, lipid-lowering drugs and antiplatelet therapy were used more often by males, with women predominating in the prescription of diuretics and angiotensin receptor blockers and anticoagulants, (P<.05).The proportion of patients with blood pressure<140/90mmHg was 60.5% and 59.1%, and that of LDL-cholesterol <100mg/ dl was 40.4% y 31% (P<.005), in males and females, respectively.
ConclusionsIn almost all the 20,000 patients with CVD studied, substantial gender differences in the prevalence, therapy and achievements of goals in the different types of CVD were observed. These results suggest the convenience of homogenization of the computerized registries at the present, for monitoring results over time, with no need of continuous sampling-based studies.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<