Evaluar, en los pacientes nonagenarios de la comunidad, la influencia de haber padecido un accidente vascular cerebral (AVC) o una fractura de fémur.
MétodosSe evaluó un total de 128 nonagenarios no institucionalizados (edad media 93,05±3,1 años). Se valoró la mortalidad total y la pérdida funcional después de dos años de seguimiento.
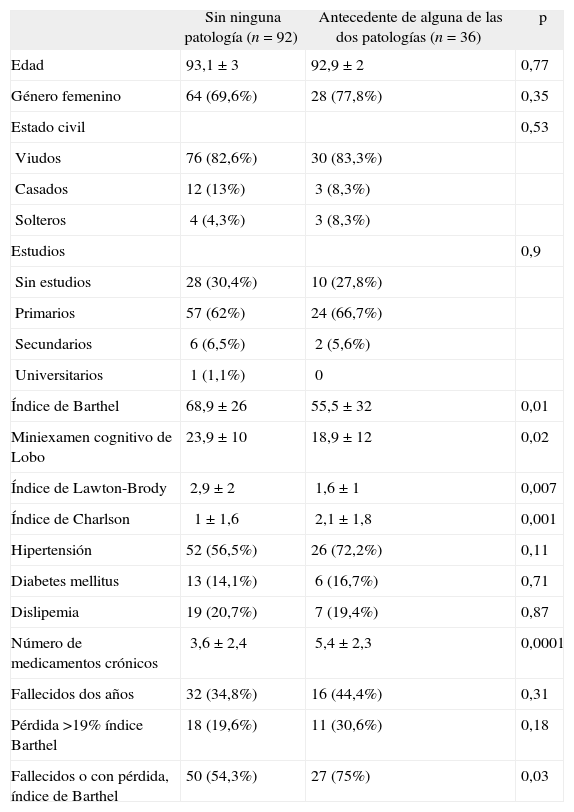
ResultadosCuarenta y ocho pacientes (37,5%) fallecieron, y existía una pérdida funcional en 29 (36,2%) de los 80 pacientes supervivientes. En 77 (60,2%) pacientes existía una mala evolución entendida como fallecimiento o pérdida funcional. En los pacientes con antecedentes de AVC o fractura de fémur existía una peor evolución global (mortalidad o pérdida de funcionalidad) que en los que no tenían (p=0,03).
ConclusionesEn los pacientes nonagenarios que viven en la comunidad con antecedentes de fractura de fémur y/o AVC existe una peor evolución entendida como la existencia de mortalidad o pérdida funcional a los dos años de seguimiento.
To evaluate in community-dwelling nonagenarians the influence of having previously suffered a stroke or a hip fracture.
Methods128 nonagenarians (mean age was 93.5±3.1 years) who were living in their own homes were evaluated prospectively. We evaluated total mortality and functional decline after two years of follow-up.
ResultsForty-eight patients (37.5%) died, and in 29 (36.2%) of the 80 surviving patients there was a functional decline. In 77 (60.2%) patient a bad clinical course was collected (death or functional decline). In the patients with prior stroke or hip fracture there was a worse overall clinical course (mortality or loss of functionality) than in the remaining patients (p=0.03).
ConclusionsCommunity-dwelling nonagenarians with a stroke or hip fracture history underwent a worse clinical course (mortality and functional decline) after two years of follow-up.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<