Hypoglycemia can negatively impact many aspects of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) management. The aim was to determine the impact of hypoglycemia and the fear for hypoglycemic episodes on HRQoL in T2DM patients in Spain, as well as healthcare professionals’ attitudes and knowledge of these issues.
Patients and methodsAn observational, cross-sectional study, with consecutive recruitment of T2DM patients in 661 healthcare centers, between September 2010 and May 2011. Sociodemographic and clinical variables were recorded. HRQoL (ADDQoL questionnaire) and fear for hypoglycemia (HFS-II) were evaluated. Two groups were compared: with and without reported hypoglycemia in the previous 6 months. Physicians responded 4 questions (visual analog scales).
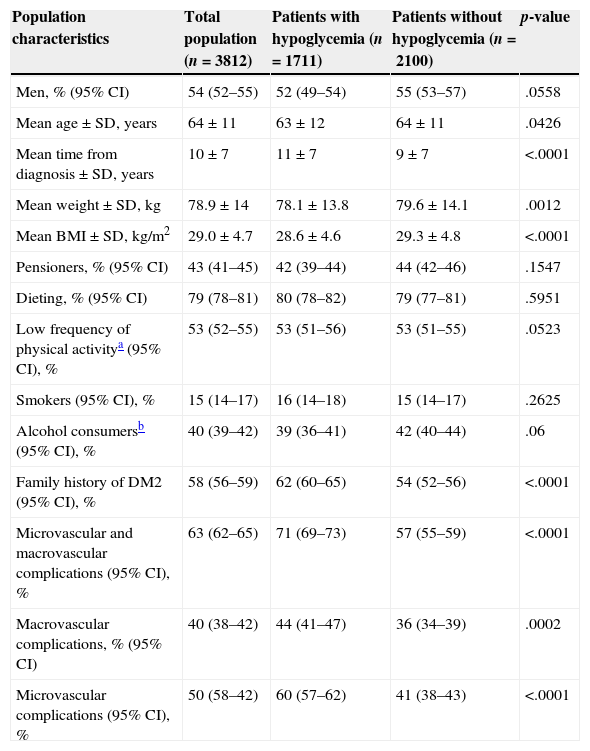
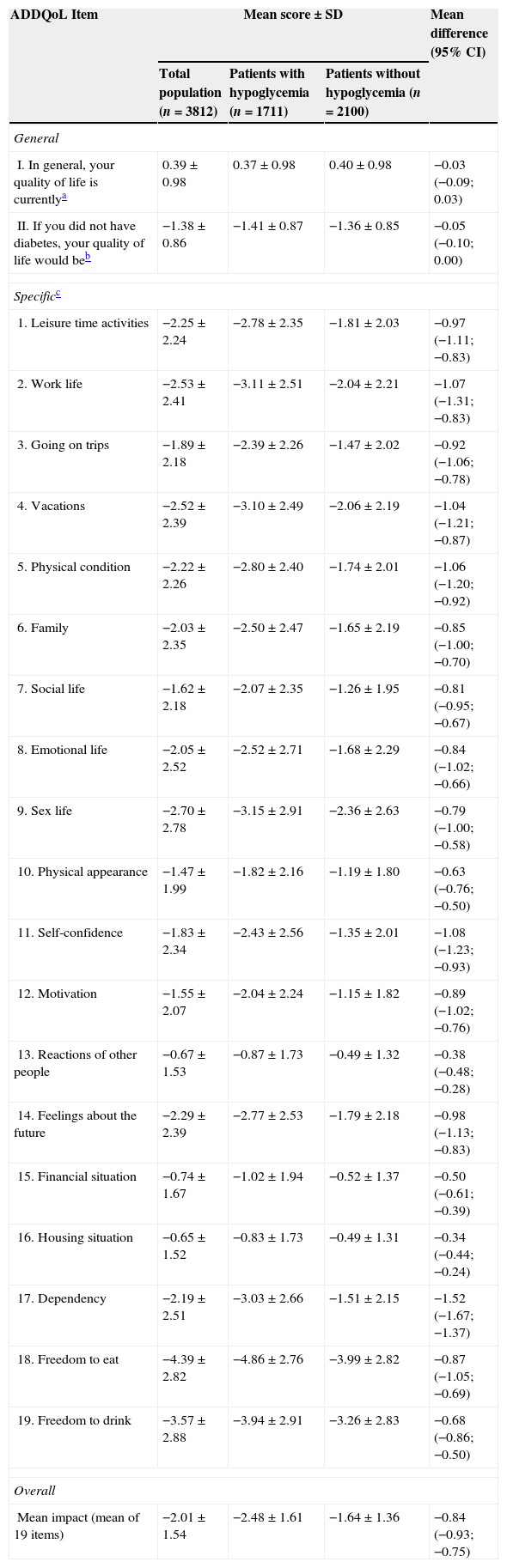
Results4.054 patients participated, of which 3812 were selected [mean age (SD)=64 (11) years; male=54%; 10 (7) years for diagnostic of T2DM]. Patients with hypoglycemia (45%) expressed higher fear for hypoglycemia [31.32 (15.71) vs. 18.85 (16.03); p<.0001] and the overall impact of T2DM on their HRQoL was more negative [−2.48 (1.61) vs. −1.64 (1.36); p<.001]. Respondent physicians occasionally used HRQoL questionnaires, knew about hypoglycemia risk, explored fear for hypoglycemia and modified treatments accordingly.
ConclusionsT2DM patients with hypoglycemia show an increase of fear for them, negatively affecting T2DM patients HRQoL. However physicians know the risk of hypoglycemia, they explore the fear for hypoglycemic episodes occasionally.
Las hipoglucemias pueden tener un impacto negativo en diferentes aspectos del manejo de la diabetes mellitus tipo 2 (DM2). El objetivo fue determinar el impacto que las hipoglucemias y la preocupación que generan tienen en la calidad de vida relacionada con la salud (CVRS) de los pacientes con DM2 en España, así como explorar las actitudes y conocimientos de los médicos respecto a estos aspectos.
Pacientes y métodosEstudio observacional, transversal, con reclutamiento consecutivo de pacientes con DM2 en 661 centros sanitarios, entre septiembre/2010 y mayo/2011. Se recogieron variables sociodemográficas y clínicas de los pacientes, evaluando su CVRS (cuestionario ADDQoL) y preocupación por las hipoglucemias (subescala HFS-II). Se compararon 2 grupos: con y sin hipoglucemias reportadas en los últimos 6 meses. Los médicos respondieron 4 cuestiones (escalas visuales analógicas).
ResultadosParticiparon 4.054 pacientes, de los cuales se seleccionaron 3.812 [edad media (DE)=64 (11) años; hombres=54%; 10 (7) años de diagnóstico de DM2]. Los pacientes que reportaron hipoglucemias (45%) presentaron mayor preocupación [31,32 (15,71) frente a 18,85 (16,03); p<0,0001] y el impacto global de la DM2 sobre su CVRS fue más negativo [−2,48 (1,61) frente a −1,64 (1,36); p<0,001]. Los médicos encuestados empleaban ocasionalmente cuestionarios de CVRS, conocían el riesgo de hipoglucemias, exploraban con relativa frecuencia la preocupación que generan y modificaban esporádicamente el tratamiento debido a las mismas.
ConclusionesLos pacientes con DM2 e hipoglucemias muestran mayor preocupación por las mismas, afectando negativamente su CVRS. Aunque los médicos conocen el riesgo de hipoglucemias, no suelen explorar la preocupación que generan.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<