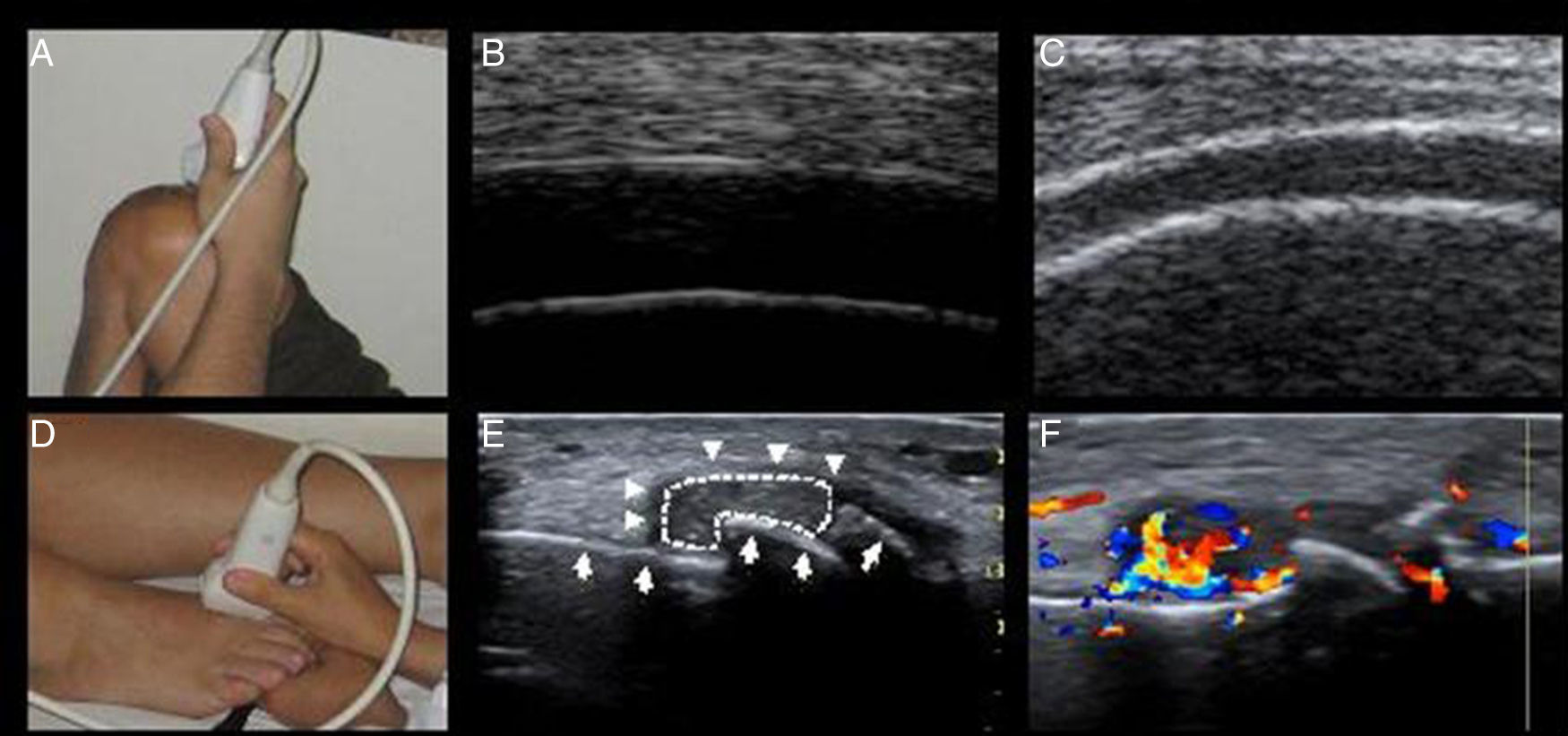
El aumento de la concentración sérica de uratos (hiperuricemia, mayor o igual a 7,0mg/dL) ocasiona cristales que promueven inflamación y lesión articular. La ecografía puede poner de manifiesto estos depósitos de urato. Su presencia obliga a considerar que un paciente con hiperuricemia en realidad padece gota asintomática, y que un enfermo con gota sin tofos subcutáneos puede tener gota tofácea. La información que ofrece la ecografía (signo del «doble contorno» y de concreciones hiperecogénicas simulando nubes) posibilita una clasificación de la hiperuricemia y de la gota más precisas. Además, esta información puede dar lugar a modificaciones relevantes en cuanto al proceder diagnóstico y terapéutico en los enfermos con hiperuricemia y gota.
The increase in serum urate concentrations (hyperuricaemia, ≥7.0mg/dL) creates crystals, which promote inflammation and joint lesions. Ultrasonography can reveal these urate deposits. The presence of crystals suggests that a patient with hyperuricaemia is actually experiencing asymptomatic gout, and that a patient with gout without subcutaneous tophi could experience tophaceous gout. The information offered by ultrasound (double contour sign and hyperechoic concretions mimicking clouds) enables a more specific classification of hyperuricaemia and gout. Additionally, this information can lead to relevant changes in terms of the diagnosis and therapeutic approach for patients with hyperuricaemia and gout.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<