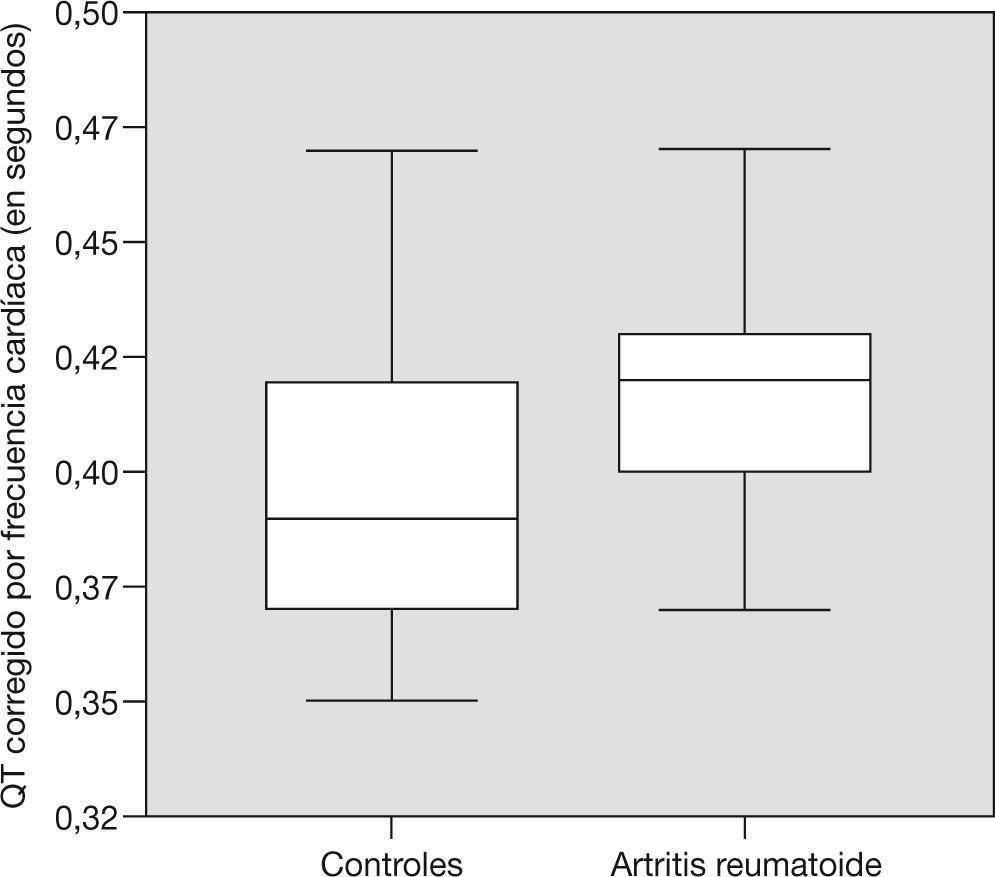
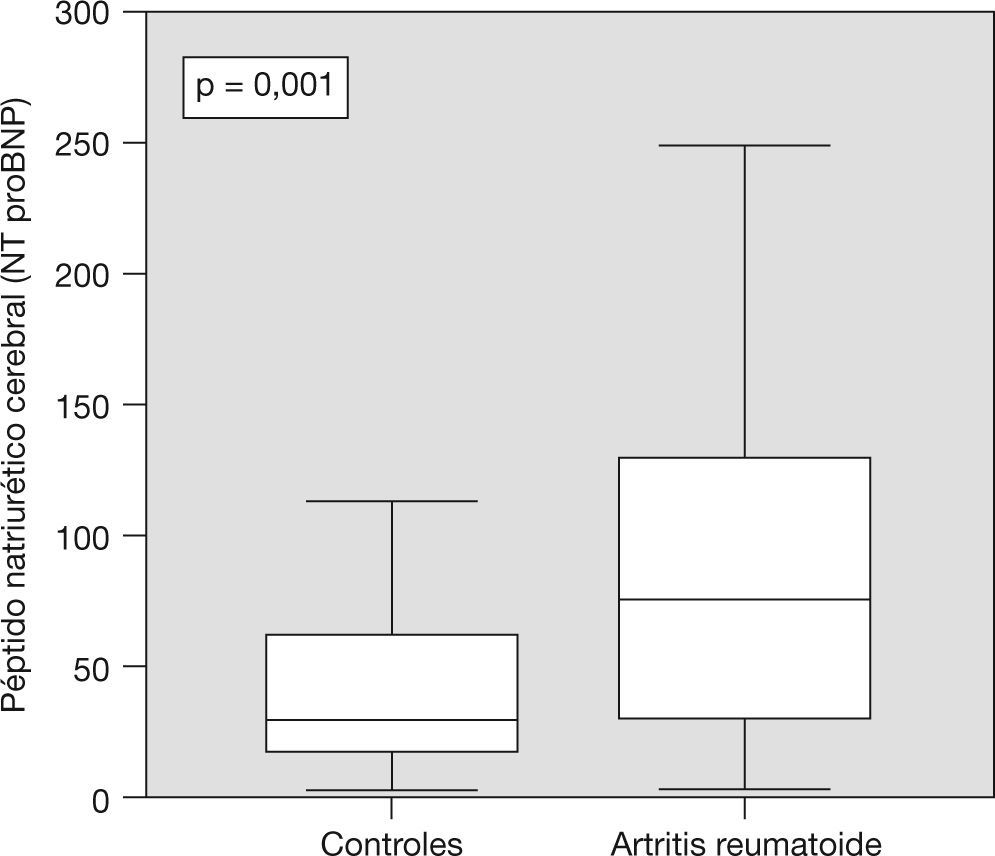
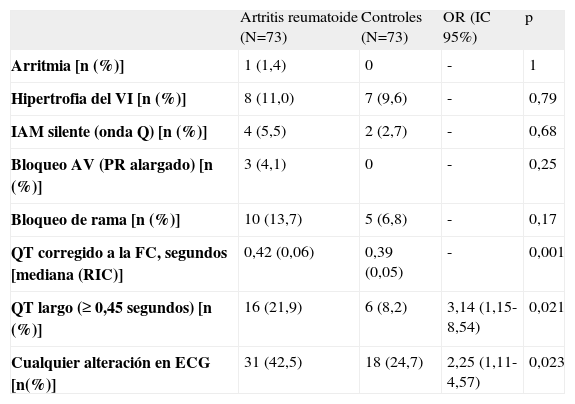
En la artritis reumatoide (AR) existe un incremento de la morbimortalidad cardiovascular que se ha relacionado con la inflamación sistémica. Nuestro objetivo fue analizar la calcificación coronaria detectada por la tomografía computarizada multicorte y la disfunción miocárdica subclínica mediante el péptido natriurético cerebral o tipo B (BNP) y el electrocardiograma en pacientes con AR, así como su relación con las características de la enfermedad. Se estudiaron 73 pacientes con AR y 73 controles con artrosis, sin historia de enfermedad vascular. Los pacientes con AR presentaron un score de calcio coronario alto con mayor frecuencia que los controles (19,2% frente a 11%; p = 0,17), que se relacionó con el tiempo de evolución de la enfermedad (p = 0,003). La concentración de BNP fue superior en el grupo con AR (90,0 frente a 45,4; p = 0,003), así como el tamaño del QT corregido, la frecuencia de un QT largo y el hallazgo de infarto silente. En conclusión, los pacientes con AR presentan calcificaciones coronarias con mayor frecuencia que la población general y muestran más signos bioquímicos y electrocardiográficos de disfunción miocárdica subclínica.
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterized by high cardiovascular (CV) mortality, which has been related to systemic inflammation. Our aim was to analyze coronary calcification by computed tomography and subclinical myocardial dysfunction evaluated by brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) levels and an electrocardiogram in RA patients and its relationship with disease characteristics.
Seventy-three RA patients and same number of controls formed by osteoarthritis patients were studied, all without a background of cardiovascular clinical events. RA patients had a higher calcium score than the control group (19.2% vs. 11%; p = 0.17)), this being associated with disease duration. BNP levels (90.0 vs. 45.4; p = 0.003), corrected QT length, large QT frequency and silent myocardial infarct were higher in the RA group. In conclusion, RA patients showed more coronary calcification frequency than in general population and more biochemical and electrocardiogram myocardial subclinical dysfunction signs.
Article
Diríjase desde aquí a la web de la >>>FESEMI<<< e inicie sesión mediante el formulario que se encuentra en la barra superior, pulsando sobre el candado.

Una vez autentificado, en la misma web de FESEMI, en el menú superior, elija la opción deseada.

>>>FESEMI<<<